The MOSINCO project will improve the way composite parts are manufactured and maintained, leading to better quality control, safety and traceability.
The GAIKER technology centre, a member of the Basque Research & Technology Alliance (BRTA), is leading the MOSINCO project, the main aim of which is to develop new technologies to allow the contactless monitoring of composite materials, from the manufacturing process to the end of their useful life. Its ultimate goal is to ensure the quality, safety and traceability of parts, while reducing defects, maintenance costs and waste.
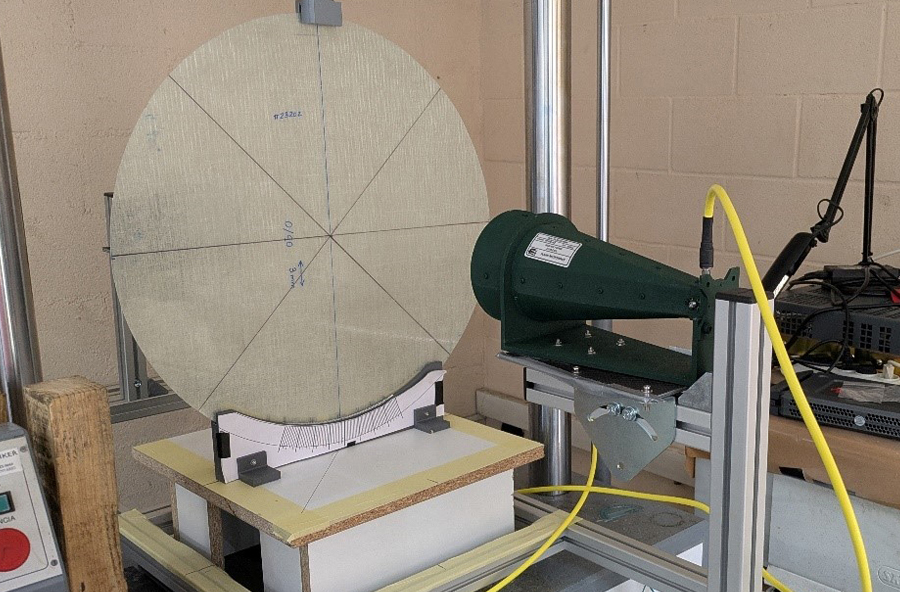
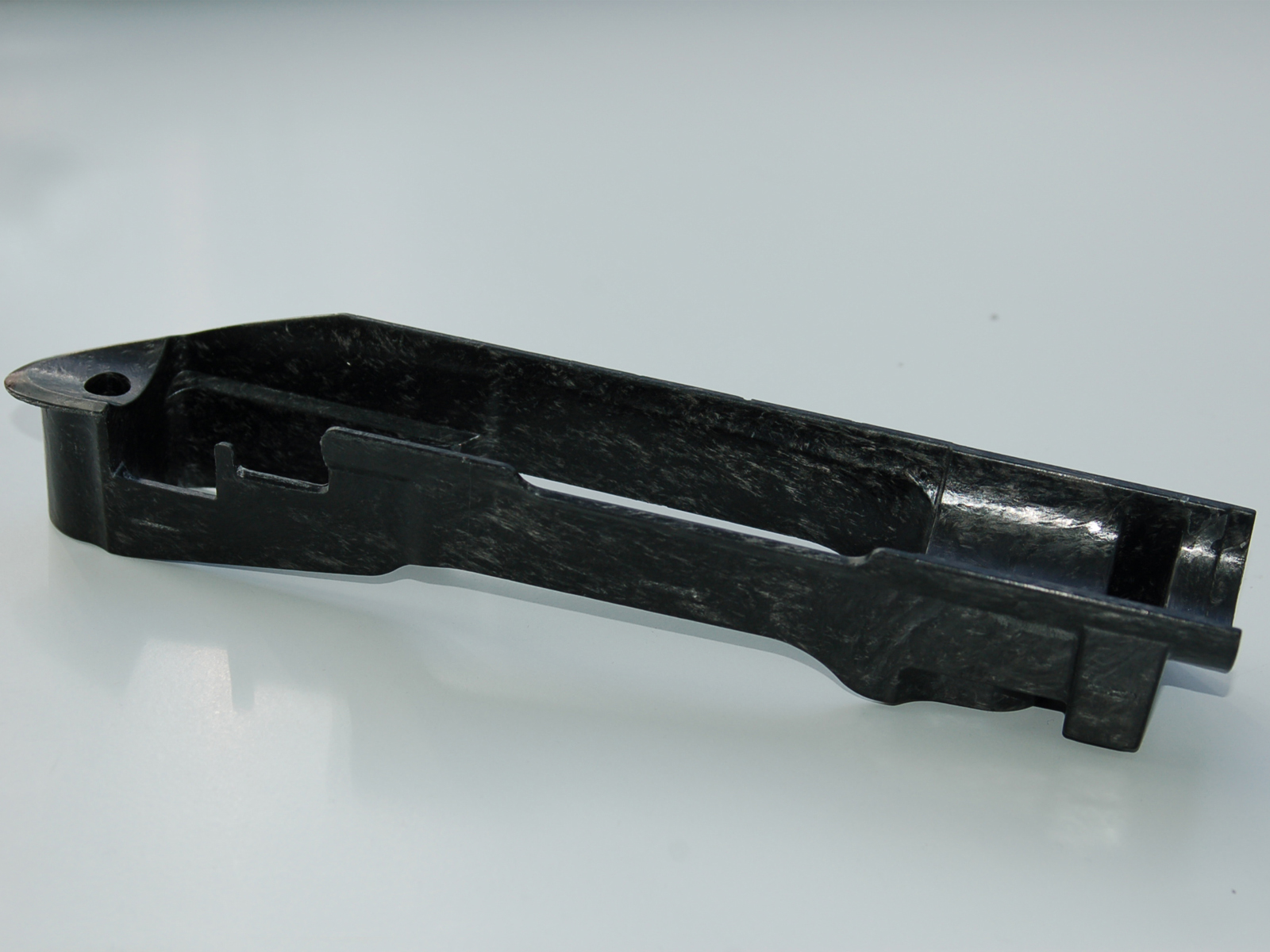
The aim of this research is to open the door to a new generation of smart composites with self-diagnostic capabilities and optimise their maintenance so as to avoid routine, costly inspections. The idea is to improve the manufacturing efficiency and structural properties of parts, using less material. To achieve this, work is being done on developing and integrating three technological lines. First, magnetic microwires embedded in the materials are used to detect deformations, stresses and strains and temperature changes. Second, air-coupled ultrasound (ACU) are used to detect defects and evaluate the curing of the material during manufacture. And finally, functional inks, which change colour with temperature, making it possible to control the curing process or unequivocally identify each part. The potential of these three technologies is analysed in the project both individually and by identifying the possible synergies between them.
Funded by the Basque Government as part of its ELKARTEK 2024 programme of aid for collaborative research in strategic areas, MOSINCO involves six different entities including Autotech (Gestamp), BCMaterials, EHU, Ideko, the University of Deusto and the GAIKER Technology Centre, which is responsible for coordinating the consortium's activities, ensuring that the technologies are aligned with the needs of industry. The centre is also working on developing and validating new sensorised materials and will ensure that monitoring systems are integrated throughout the life cycle.
This research represents a qualitative leap in the way composite parts are manufactured and maintained, as these new technologies will improve quality control, thereby reducing defects and waste, safety and reliability for sectors such as aeronautical and automotive industries. Ultimately, it will be a step towards a smarter, more efficient and sustainable industry.

Subsidised by the Basque Government